- Install SubGit tool according to the Installation guide.
- Configure GitLab server:
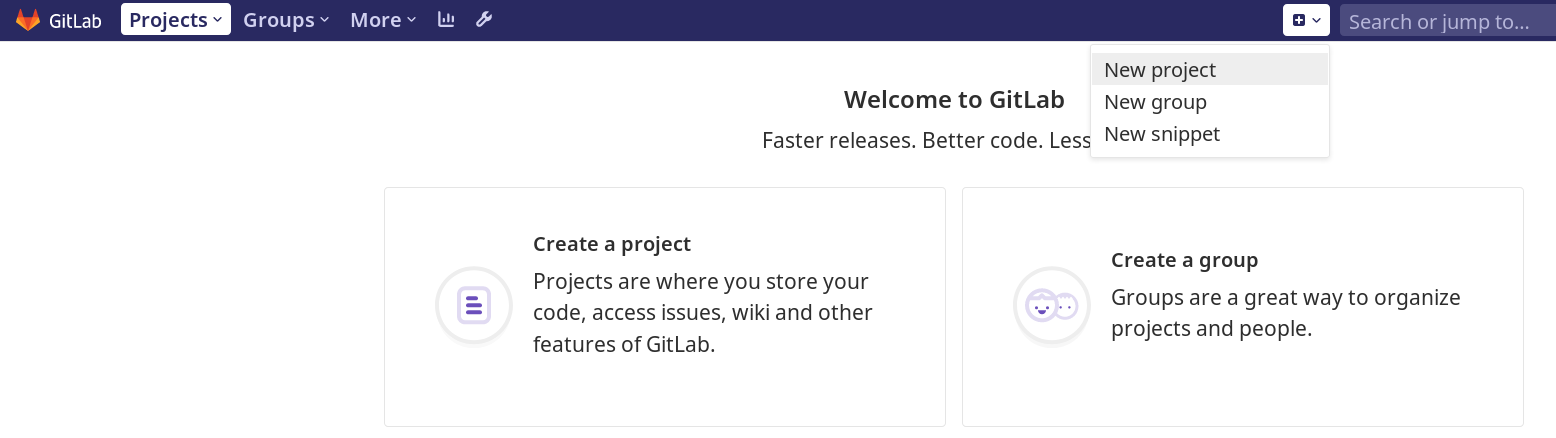
- Login to GitLab web GUI and create a new project:
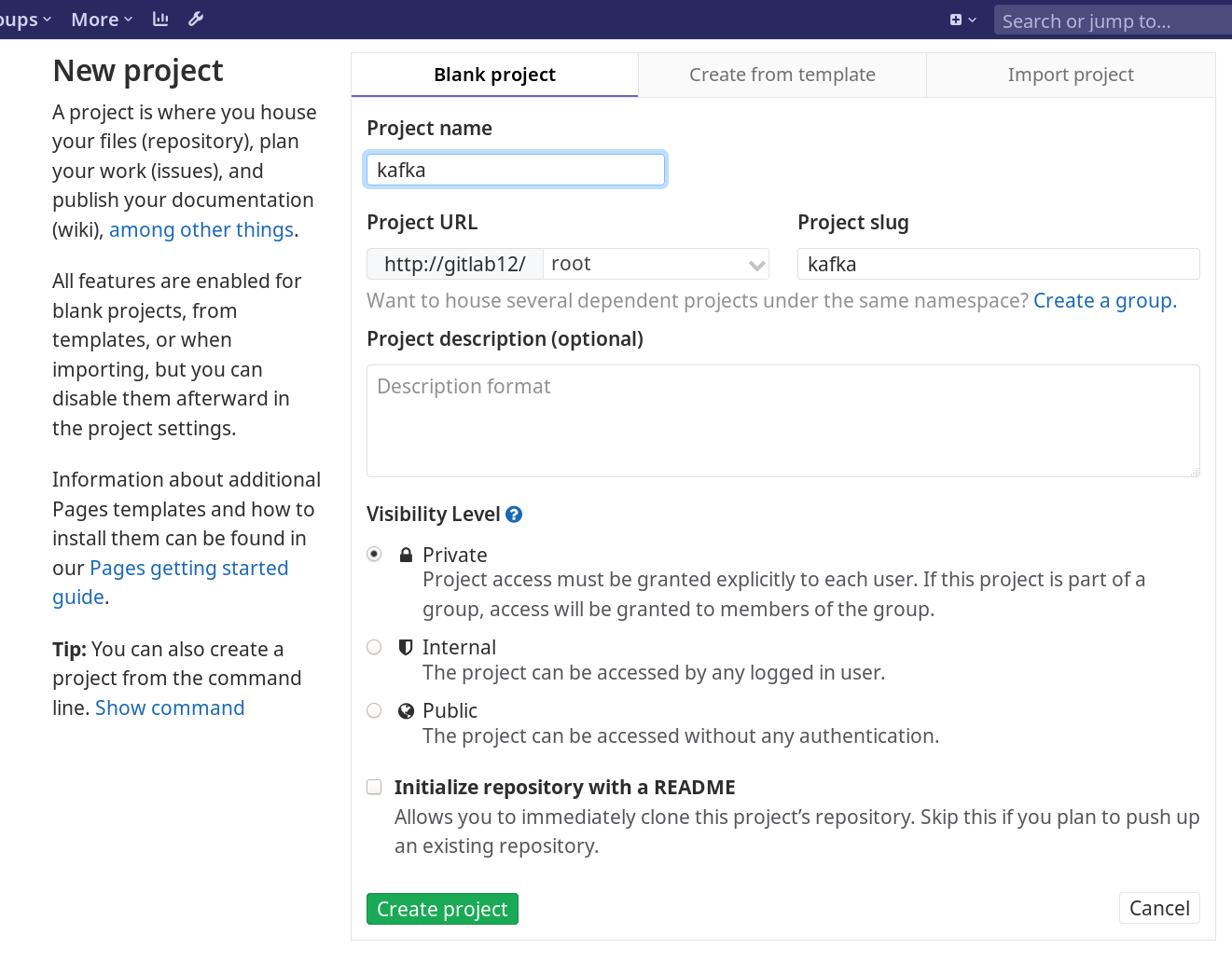
Give a name to your project, do not check “Initialize repository with a README” checkbox, and click Create project button.
- Login to GitLab web GUI and create a new project:
- Configure the repository:
Change identity to 'git' user:
change identity to git user$ su git
Change directory to that one that contains the newly created project.
Older versions of GitLab stored projects in
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/<username>
where <username> was the GitLab username that had been used during the project creation on step 1.
Since version 10.0 GitLab uses hashed storage as follows:
/var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/@hashed/<hash[0..1]>/<hash[2..3]>/<hash>.git
To find the repository path in GitLab v.10+, follow this guide.
Navigate to that directory:
change directory$ cd /var/opt/gitlab/git-data/repositories/<repo_path>
Perform initial import configuration:
$ subgit configure --layout auto --trunk TRUNK SVN_URL GIT_REPO
where
SVN_URL– SVN project URL.GIT_REPO– a path to new Git repository.TRUNK– a path, relative toSVN_URL, that leads to an SVN directory that plays a role of the main line of development.
Specify authors mapping.
Configure authors mapping in the default authors mapping file:GIT_REPOS/subgit/authors.txt
Or change
core.authorsoption so that it points to the global authors mapping file.
Find more details about authors mapping in Authors mapping article.
- Perform import and start using the new Git repository:
Import data to the repository by the command:
$ subgit import GIT_REPO
When the command completes, you can clone your new Git repository and start to work with it:
$ git clone GITREPO WORKTREE
where
WORK_TREE– a path to your working copy.Empty working tree case
If Git warns you that you are cloning an empty repository and you don't see your files in the working tree, most probably automatic branches and tags mapping didn't work correctly. In this case, mapping has to be set manually, see details on mapping in Branches and tags mapping.
- Get support:
If you run into any problems, see one of the following guides for more details:
Note:
For one-time import, no license is needed.
Should you need assistance, don't hesitate to contact us at support@tmatesoft.com.